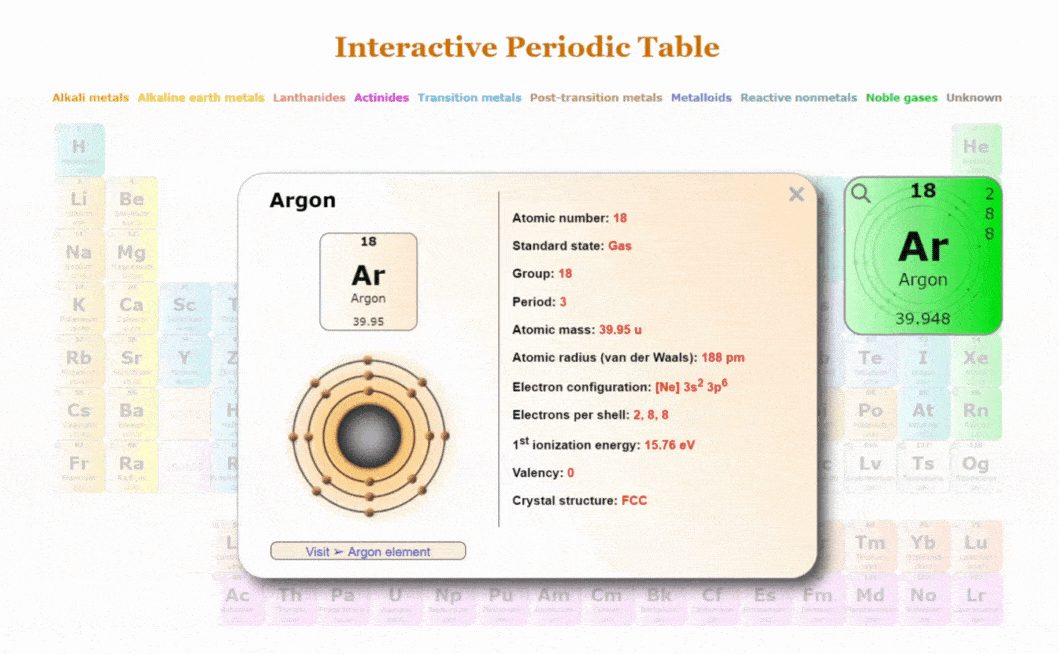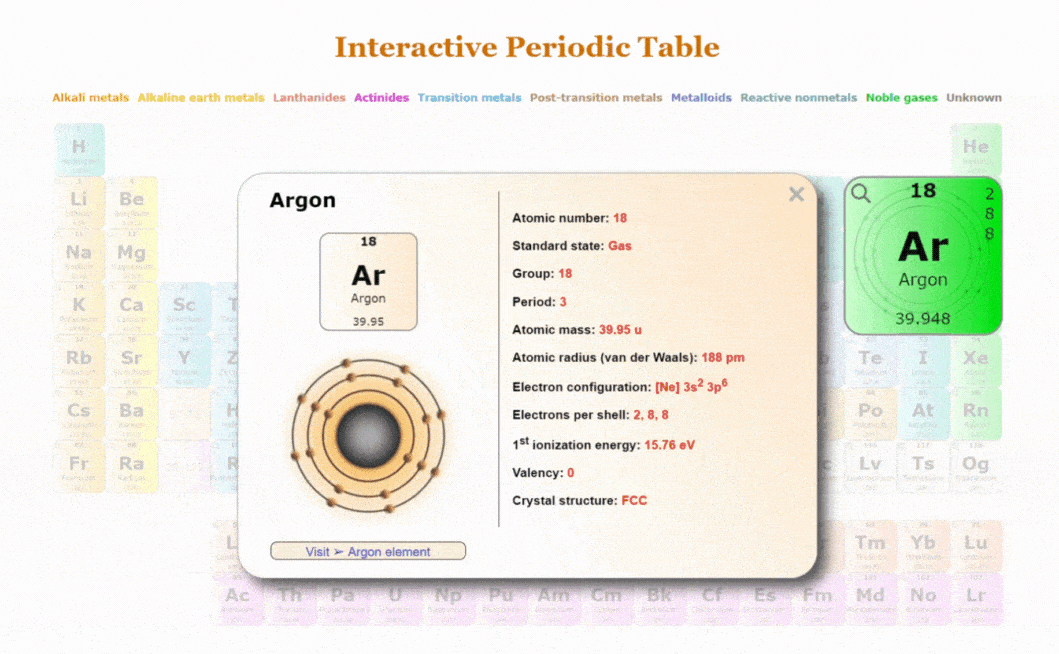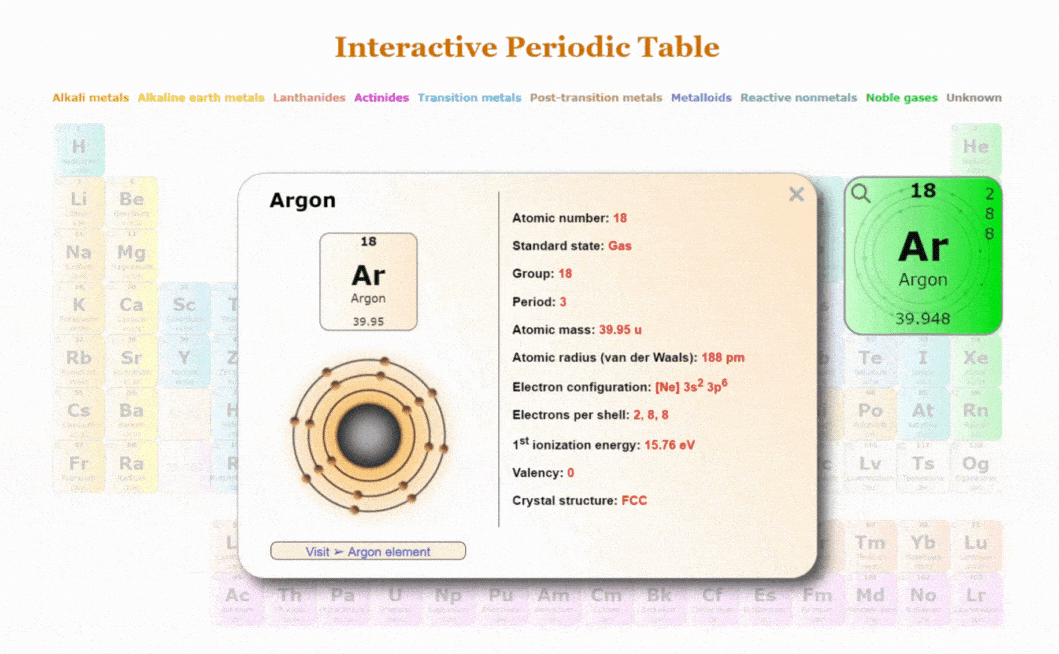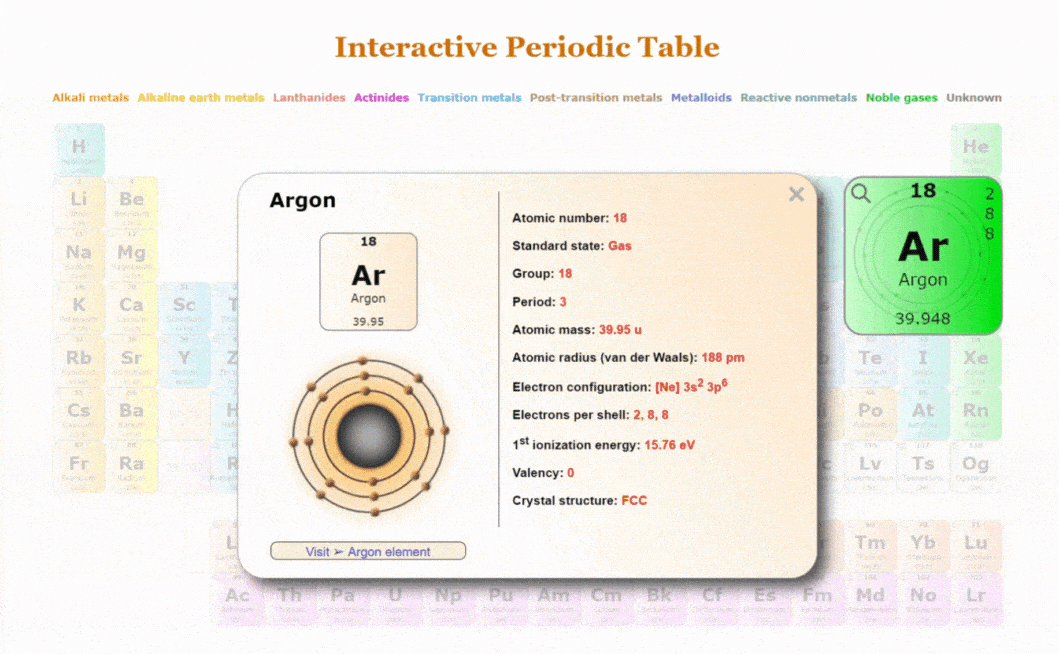
Introduction to the Periodic Table
The periodic table is a crucial tool in the field of chemistry. It organises all known chemical elements based on their atomic number, electron configurations, and recurring chemical properties. Its relevance extends beyond the confines of science classrooms, influencing industries such as pharmaceuticals, materials science, and environmental science.
Structure and Organisation of the Periodic Table
The periodic table consists of rows called periods and columns known as groups or families. Elements are arranged sequentially by their atomic number from left to right. Notably, elements within the same group share similar chemical properties. The table also categorises elements into metals, non-metals, and metalloids, providing a clear pathway to understanding their behaviour.
Recent Developments and Discoveries
In recent years, advancements in the understanding of elements have led to the discovery of new synthetic elements. For instance, elements such as Oganesson (Og) and Moscovium (Mc) have been added to the periodic table, showcasing that our understanding of matter continues to evolve. Researchers are studying the properties of these elements, which may lead to breakthroughs in technology and medicine.
Significance for Future Generations
The periodic table not only enhances our understanding of the natural world but also serves as a foundational tool for future scientific innovations. Its systematic approach lays the groundwork for the development of new materials that can revolutionise industries from electronics to renewable energy. As we face challenges such as climate change, the study of the periodic table may play a pivotal role in finding sustainable solutions.
Conclusion
Overall, the periodic table remains a powerful symbol of scientific achievement and discovery. Its ongoing relevance in research and application highlights the importance of chemistry in our daily lives. For students and professionals alike, the periodic table provides a framework that encourages inquiry and innovation, shaping the future of science and technology.