Introduction
Inflation has been a pressing concern for economies around the globe in 2023, significantly affecting consumer purchasing power and economic stability. As governments and financial institutions grapple with rising prices, understanding the causes and consequences of inflation is essential for both policymakers and consumers alike. This article delves into the current trends in inflation, exploring its implications for various sectors and the overall economy.
Current Inflation Trends
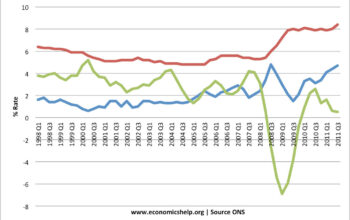
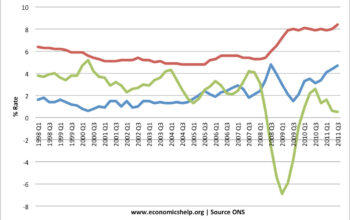
As of October 2023, inflation rates across many countries remain elevated, with the United Kingdom reporting an annual inflation rate of approximately 6.7%, according to the Office for National Statistics. This marks a gradual decline from a peak of over 10% in late 2022, yet the rate is still above the Bank of England’s 2% target. High energy prices, increased raw material costs, and lingering supply chain disruptions, exacerbated by the aftermath of the COVID-19 pandemic, continue to drive inflationary pressures. Additionally, wage growth has not kept pace with price increases, leading to a real reduction in household income.
The Impact on Consumers
The rise in inflation has palpable effects on consumers, who find themselves paying more for everyday goods and services, from groceries to transportation. In terms of purchasing power, higher inflation can erode savings and undermine financial security for families across the country. Essential items such as food and fuel have seen the most significant price hikes, prompting many households to adjust budgets and prioritise spending. According to a recent survey conducted by the Bank of England, nearly 70% of respondents reported changing their shopping habits due to rising prices.
Government Responses
In response to the inflation crisis, central banks, including the Bank of England and the Federal Reserve in the United States, have implemented interest rate hikes in efforts to combat inflationary pressures. The aim is to reduce consumer spending and borrowing, thereby cooling down the economy. However, these actions carry risks as well; higher interest rates may lead to lower economic growth and increased costs for businesses, particularly those reliant on loans for operations and expansion. The delicate balance between curbing inflation and fostering economic growth poses a significant challenge for policymakers.
Conclusion
As we navigate through 2023, inflation remains a critical issue impacting economies worldwide. While some signs suggest moderating inflation rates, persistent challenges in supply chains and energy prices contribute to uncertainty in future economic forecasts. Homeowners, consumers, and investors must remain vigilant as they adjust to the evolving economic landscape. Understanding inflation and its effects will help individuals make informed decisions in their financial planning and investment strategies in these uncertain times.