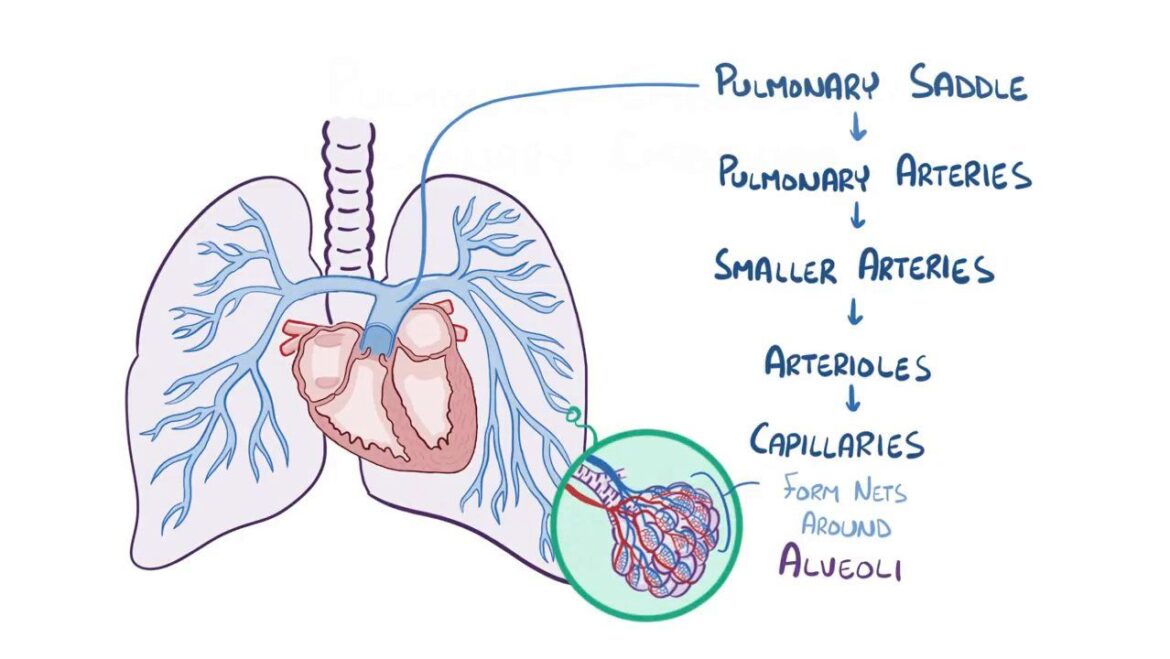
Introduction
Pulmonary embolism (PE) is a serious medical condition that occurs when a blood clot blocks a blood vessel in the lungs. This condition is critical as it can lead to severe complications, including death, if not promptly diagnosed and treated. According to the NHS, approximately 25,000 people in the UK are diagnosed with pulmonary embolism each year, making awareness and education on the topic vital for public health.
Understanding Pulmonary Embolism
Pulmonary embolism arises primarily from deep vein thrombosis (DVT) when a clot, usually formed in the legs, dislodges and travels to the lungs. Common symptoms include sudden shortness of breath, chest pain that may worsen with deep breaths, coughing up blood, and rapid heartbeat. The severity of symptoms can vary widely among individuals.
Risk Factors
Several factors increase the risk of developing pulmonary embolism. These include prolonged immobility (such as long-haul flights), recent surgery, particularly in the legs or pelvis, and certain medical conditions like cancer, heart disease, or previous instances of DVT or PE. Additionally, lifestyle factors such as smoking, obesity, and hormonal therapies can further heighten risk levels.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Timely diagnosis of pulmonary embolism is crucial. Healthcare providers utilize various methods such as blood tests (D-dimer), imaging tests including CT pulmonary angiography or ultrasound, and patient history assessments to diagnose PE effectively. Treatment options depend on the severity of the condition and can include anticoagulants, thrombolytics for severe cases, and surgical interventions in critical situations.
Conclusion
Awareness of pulmonary embolism’s symptoms and risk factors is essential in reducing mortality associated with this condition. Those at risk should consider regular check-ups and discussions with healthcare professionals about preventative measures. As research advances, understanding and treatment protocols are expected to improve, leading to better outcomes for patients. Individuals must remain informed and attentive to their health to mitigate the potential dangers of pulmonary embolism.