Introduction
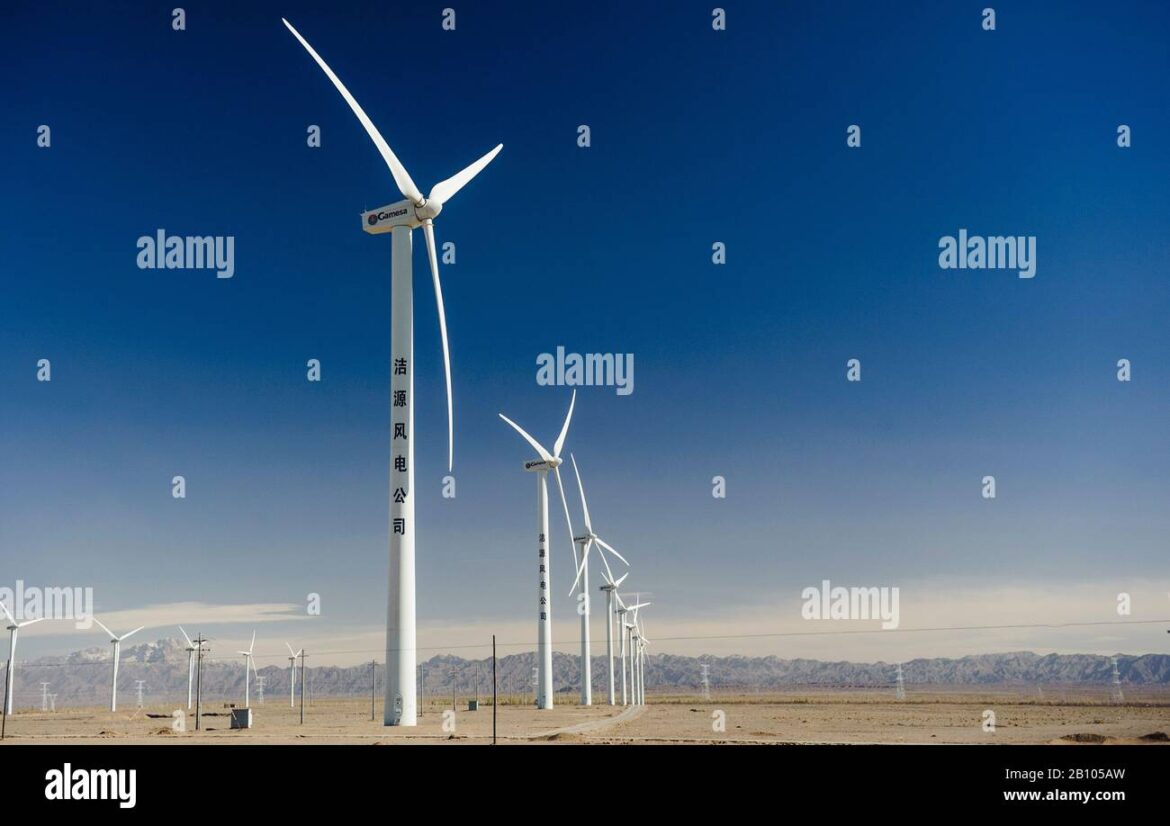
As the world shifts towards renewable energy, China is leading the charge with its extensive network of wind farms. Wind energy is not only crucial for achieving national targets on carbon emissions but also plays a significant role in enhancing energy security and economic growth. With a remarkable increase in installed capacity, China’s wind farms are becoming a focal point in the global renewable energy landscape.
Current Landscape of Wind Energy in China
According to the National Energy Administration (NEA), as of 2022, China boasted over 300 gigawatts (GW) of installed wind power capacity, solidifying its position as the world’s largest producer of wind energy. Recent statistics indicate that in 2022 alone, China added about 47 GW of new wind power capacity, showing an increase from the previous year. Various regions, especially Inner Mongolia, Xinjiang, and Gansu, have emerged as primary hubs for wind power due to their favourable geographical conditions.
Government Initiatives and Investments
The Chinese government has implemented policies to promote the development of wind energy, including subsidies, grid infrastructure enhancements, and incentives for technology research and development. The 14th Five-Year Plan, introduced in 2021, aims to significantly increase both onshore and offshore wind power capacity, targeting around 1,200 GW of total installed wind capacity by 2030. This ambitious goal represents an increase in China’s commitment to transitioning away from fossil fuels and achieving carbon neutrality by 2060.
Challenges on the Horizon
Despite the rapid expansion of wind farms, challenges remain. Issues such as land acquisition, environmental concerns, and the need for improved transmission infrastructure could hinder further growth. Resistance from local communities and biodiversity impacts also pose significant challenges for future developments. Moreover, integrating such a high volume of renewable energy into the national grid requires meticulous planning and technological advancements.
Conclusion
China’s wind farms are at the forefront of the global renewable energy movement, representing both opportunity and challenge. The ongoing investments and technological improvements indicate a promising future. As China continues to expand its wind power capabilities, the emphasis on sustainability and environmental harmony will be more critical than ever. The implications for global energy markets, environmental stewardship, and climate change mitigation remain profound as China seeks to lead the way in renewable energy generation.